All That You Must Know About Hemangiomas
A hemangioma is a benign growth of extra blood vessels in the skin. Typically, birthmarks are more common in girls than boys, premature babies, and Caucasian children. While we don’t know the exact cause, they aren’t hereditary. Generally, hemangiomas go away on their own without much medical intervention. But if the hemangioma is growing continuously or looks unsightly, you could consider removing it through medication or surgery. Read on to learn more about hemangiomas, including infantile hemangioma treatment in India:
When Do Hemangiomas Appear?
Hemangiomas typically appear within the first weeks and grow continuously for the first 2-3 months. Over the next few months, they continue to grow, albeit slowly. Then, they continue to remain the same size for the next few months. In most cases, the hemangioma begins to shrink as the child is around one year. This continues until the child grows up to 10 years. While most hemangiomas go away during this time, some hemangiomas may leave behind a visible scar-like mark that looks odd.
Types of Hemangiomas
Capillary Hemangioma
This is a common type of hemangioma that occurs when the capillaries are tightly packed and held together by a group of tissues. A capillary hemangioma is also called superficial when developed in the skin. They are red because they are close to the skin. Hemangiomas can be small or large, flat, raised, or protruding. Some hemangiomas look like spongy masses covering the skin.
Cavernous Hemangioma
Unlike a capillary hemangioma, cavernous hemangioma is made up of larger blood vessels that are loosely packed with spaces between the blood vessels filled with blood. Such hemangiomas vary in size and can occur anywhere in the body.
Compound Hemangioma
Such hemangiomas are a mix of capillary and cavernous hemangiomas.
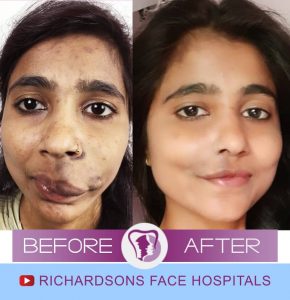
What is Infantile Hemangioma?
Infantile Hemangiomas are a type of hemangiomas found in infants – sometimes present at birth but mostly appear within the first few weeks. As with other hemangiomas, they are commonly found in girls.
Most infantile hemangiomas appear as a coloured skin patch within the first few weeks after birth. However, it grows rapidly within the first few months – by about three months of age, the hemangioma is at its maximum size.
By the time the baby is one year old, the hemangioma stops growing and even shrinks. During the involution period, the hemangioma flattens and appears less intense. This continues until the child is 3/12 to 4 years old, leaving the child with light scar tissue.
Infantile Hemangioma Treatment Options
Most infantile hemangiomas can be diagnosed through a physical examination. But the doctor may advise an ultrasound for a clear view under the skin. And if the hemangioma is large and on sensitive areas like the head or neck, the physician may suggest an MRI determine the exact size and location and look for other potential problems.
Very rarely, infantile hemangiomas could be associated with a problem called PHACE syndrome, a problem where the hemangioma could affect the brain, arteries, aorta, or eyes. This is diagnosed with a special MRI, echocardiogram, and eye exam.
Infantile hemangioma treatment options include beta-blockers like propranolol and timolol and surgery. The latter is rarely suggested but done to remove the scar that remains after the hemangioma has shrunk. Speak to an infantile hemangioma specialist in India to discuss treatment options and costs.
Visit the Richardsons Dental and Craniofacial Hospital to learn more about infantile hemangioma treatment costs in India, and schedule an initial consultation.